

We discuss the consistency of this figure with alternative evidence. 1.1 The SDSS group The US Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) aims to image 10,000.
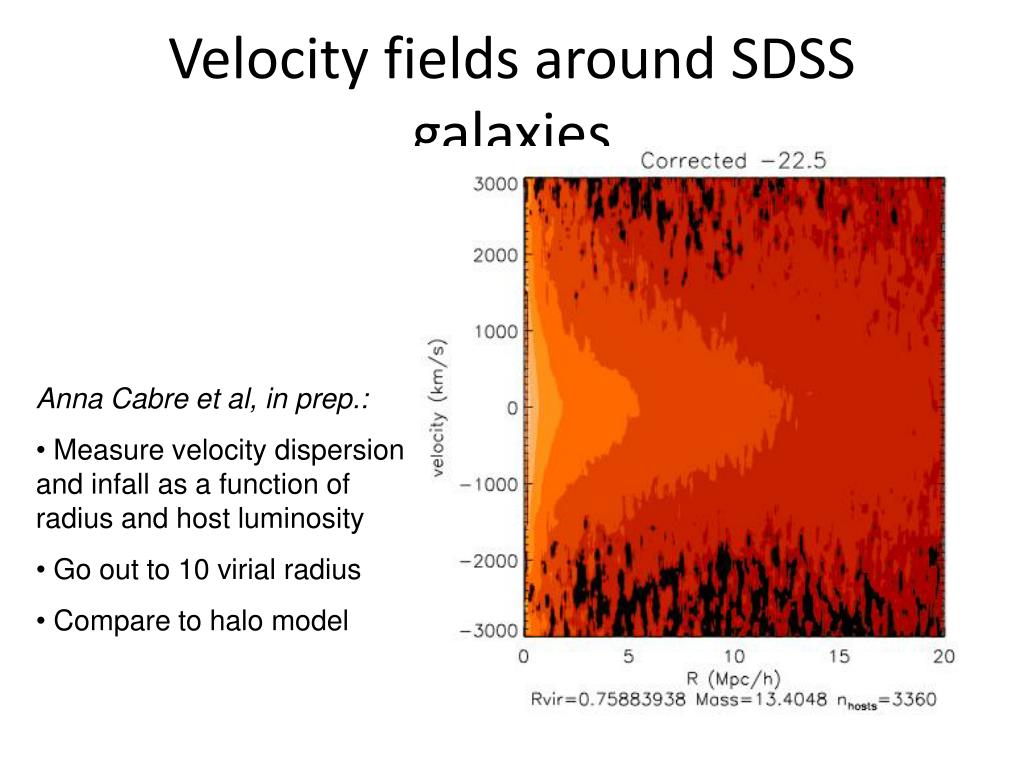
We use an ensemble of mock catalogs to demonstrate the reliability of our method. In combination with the total amplitude of CMB lensing, this favours a shift mainly in density: Ωm = 0.274 ± 0.024. Using a method to correct redshift-space distortion (RSD) for individual galaxies, we mapped the real-space distributions of galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Data Release 7 (DR7). We measure the velocity scale parameter $$\beta \equiv \sigma _8=0.297\pm 0.009$$. Here we constrain the growth rate of the structure by comparing observed Fundamental Plane peculiar velocities for 15 894 galaxies from the 6dF Galaxy Survey (6dFGS) and Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) with predicted velocities and densities from the 2M++ redshift survey. the distant-observer limit is not assumed (iii) can account for the effect of magnification and evolution bias due to a non-uniform selection function and (iv) respects the fact that observations are made on the past.
Redshift space distortions of sdss galaxies pdf#
ABSTRACT Measurement of peculiar velocities by combining redshifts and distance indicators is a powerful way to measure the growth rate of a cosmic structure and test theories of gravity at low redshift. Download PDF Abstract: We derive an analytic expression for the two-point correlation function in redshift space which (i) is nonlinear (ii) is valid on the full sky, i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
